 Introduction
Introduction
Well, I have officially signed up for my second attempt at the 100 mile distance. Lots of time though, as its not until May 2017. Regardless, I will be thinking a lot about hydration and nutrition during my training and race day and thought I would share the following with all of you. I had prepared this presentation for one of the running clinics I gave and just recently came across it; I know as runners, we are always looking for more information, so I hope it helps.
Fluid Replacement
As we
start to get into our longer runs, carrying fluids and or gels with you is
something you’ll want to start experimenting with, so that your body will be
accustomed come race day. Your
body is mostly water-between 60 and 70% and although water alone does not
provide any energy (or calories), your body requires large amounts of H2O in
order to function properly. Water regulates the core temperature of your body. I prefer to use coconut water and if you avoid the all natural variety, you will actually benefit from the ones that have the added sugar. Sugar transfers to energy. Further, try adding some tart cherry juice for the anti-inflammatory effects on the body. The added cherry juice will enhance performance by reducing muscle pain.
As
you run, your working muscles produce large amounts of heat that must be
dissipated to prevent the core temperature from rising dangerously. To
dissipate this heat, your body perspires, and loses large amounts of water. As
a runner, you should consistently hydrate yourself during both warm and cold
weather, so that you never become thirsty. By the time your thirst mechanism is
activated, your body is already suffering from dehydration-hurting your running
and putting you at risk.
You
know you're drinking enough water if you urinate about once an hour and your
urine is clear.
Prehydrating with
beverages, in addition to normal meals and fluid intake, should be initiated at least several hours before the activity to enable fluid
absorption and allow urine output to return to normal levels. The goal of
drinking during exercise is to prevent excessive (>2% body weight loss from
water deficit) dehydration and excessive changes in electrolyte balance to
avert compromised performance. Because there is considerable variability in
sweating rates and sweat electrolyte content between individuals, customized
fluid replacement programs are recommended. Individual sweat rates can be
estimated by measuring body weight before and after exercise. During exercise,
consuming beverages containing electrolytes and carbohydrates can provide benefits
over water alone under certain circumstances. Again, try coconut water, but, avoid the pulp. After exercise, the goal is to
replace any fluid electrolyte deficit. The speed with which rehydration is
needed and the magnitude of fluid electrolyte deficits will determine if an
aggressive replacement program is merited.
Depending
upon the metabolic rate, environmental conditions and clothing worn, exercise
can
induce significant elevations in body (core and skin) temperatures. Body temperature elevations elicit
 heat loss responses of increased skin blood flow
and increased sweat secretion. Sweat evaporation provides the primary avenue of
heat loss during vigorous exercise in warm hot weather; therefore
heat loss responses of increased skin blood flow
and increased sweat secretion. Sweat evaporation provides the primary avenue of
heat loss during vigorous exercise in warm hot weather; therefore
sweat losses can be substantial. Besides containing water, sweat contains electrolytes that are lost. If not appropriately replaced, water and electrolytes imbalances (dehydration and hyponatremia- is an
electrolyte disturbance in which the sodium concentration in the serum is lower than normal) can develop and adversely impact on the individuals exercise performance and perhaps health.
induce significant elevations in body (core and skin) temperatures. Body temperature elevations elicit
 heat loss responses of increased skin blood flow
and increased sweat secretion. Sweat evaporation provides the primary avenue of
heat loss during vigorous exercise in warm hot weather; therefore
heat loss responses of increased skin blood flow
and increased sweat secretion. Sweat evaporation provides the primary avenue of
heat loss during vigorous exercise in warm hot weather; therefore sweat losses can be substantial. Besides containing water, sweat contains electrolytes that are lost. If not appropriately replaced, water and electrolytes imbalances (dehydration and hyponatremia- is an
electrolyte disturbance in which the sodium concentration in the serum is lower than normal) can develop and adversely impact on the individuals exercise performance and perhaps health.
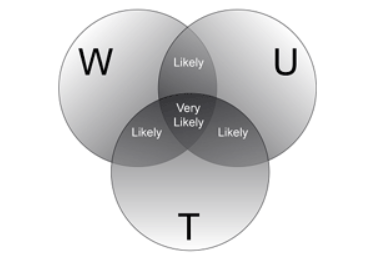
WUT you looking at?
So, the good news is that there are three reasonably good and practical markers available to you
to help you monitor your hydration status. But, because none of these indicators are entirely accurate on their own, some clever people in the US Army came up with the idea of combining all three measures to produce a more reliable rating scale called the WUT system (Weight, Urine, Thirst). This establishes the likelihood of you being euhydrated (‘well hydrated’) or hypohydrated (‘dehydrated’).
Essentially their suggestion is to monitor your body weight, the colour of your urine and how thirsty you are first thing each morning. The ‘first thing in the morning’ element is important as it limits the influence of other factors that interfere with hydration status as the day progresses.
You then feed the results into a simple Venn diagram to give you an indication of whether hypohydration is unlikely, likely or very likely as you begin that day.
The data you need to collect each morning is:
- Your body weight. Ideally as soon as you get out of bed, before eating, drinking or going to the bathroom. A loss of 2% or more of your body weight is deemed significant.
- A rating of the colour of your urine (is it light or dark in colour)
- A rating of your sensation of thirst (thirsty or not thirsty)
If 1 or less of the 3 scores you collect are ‘positive’ (i.e. body weight is within 2% of normal and/or urine is light and/or and you're not thirsty), then hypohydration (‘dehydration’) would be deemed unlikely.
If 2 out of the 3 are positive, then hypohydration would be considered ‘likely’ and this might impact your fluid intake and training plans for the day, especially if you were planning very hard or prolonged exercise in the heat.
If 3 out of the 3 are positive then hypohydration is very likely and therefore strong consideration should be given to correcting that before you undergo strenuous exercise or expose yourself to further large sweat losses.
 |
See link for more details: http://www.precisionhydration.com/blogs/hydration_advice/116318276-how-to-tell-if-you-re-dehydrated
Pre-Race Fueling
The
ideal pre-competition meal is palatable, well-tolerated and high in
carbohydrate. Athletes who
forgo eating prior to exercise because of unpleasant symptoms, as well as those looking simply to fine-tune their food selections, may benefit from experimenting with the glycemic index (GI). The GI, is system that ranks carbohydrate-rich foods according to their impact on the body’s blood sugar level, may be a useful tool when it comes to fueling up before you head to the line.
forgo eating prior to exercise because of unpleasant symptoms, as well as those looking simply to fine-tune their food selections, may benefit from experimenting with the glycemic index (GI). The GI, is system that ranks carbohydrate-rich foods according to their impact on the body’s blood sugar level, may be a useful tool when it comes to fueling up before you head to the line.
It was thought that runners needed to avoid eating large amounts of carbohydrate-rich foods prior to
exercise. The inevitable “sugar high” would be promptly followed by a performance-busting crash in
blood sugar (hypoglycemia), leaving you feeling shaky, weak and unable to concentrate. On the other
hand, a pre-race carbohydrate-rich meal, particularly before prolonged endurance events, such as a
marathon, has been shown to enhance performance. Eating a meal, especially before a morning race,
helps ward off hunger pangs, restocks liver glycogen (stored carbohydrate) which fuels your brain
during exercise and it provides valuable energy for muscles during intense exercise lasting an hour or
longer.
The GI ranks carbohydrate-rich foods compared to glucose-a simple sugar with a GI ranking of
100.Carbohydrate-rich foods and beverages that enter the bloodstream rapidly following ingestion earn
a high GI (above 75) whereas foods that enter the bloodstream slowly have a low GI (below 60).
Choosing a low-GI carbohydrate food before exercise may enhance endurance by producing a slower,
more sustained release of glucose into the bloodstream. The reasoning is: carbohydrate-rich foods and
beverages trigger the release of the hormone insulin. Insulin directs the liver and muscle cells to
remove glucose from the blood and store it as glycogen. A slower, sustained release of glucose will
temper the insulin surge that follows, reducing the chance of the body “over-correcting” as it races to
lower the body’s blood sugar level back to a normal range.
A small percentage of athletes who are sensitive to swings in blood sugar following pre-exercise meals
will experience central nervous symptoms or premature muscular fatigue which are indicative of
hypoglycemia. Feeling light-headed, shaky or weak and sweating profusely as you begin to exercise
are classic signs. Therefore, experiment with both high and low index meals in training to assess what
works best for you. Runners who wish to fine-tune their food choices before prolonged events, like
the marathon or those that are sensitive to decreases in blood sugar, should benefit the most from
manipulating the glycemic index of their pre-exercise meal.
Runners may be able to improve their competitive performances by consuming lower GI foods due to
the sustained release of glucose that these foods promote. For me, I notice the benefits of eating an
apple about a half hour prior to racing; in fact, it has become a bit of a ritual.
Be sure to try different hydration and nutrition methods during training, so that there are no surprises on race day.
Happy Trails My Friends
Happy Trails My Friends






